
Antioxidant BHT 264
CAS:128-37-0
Purity:99%
Contact Now
We will contact you as soon as possible
Your Location:Home >Products >Intermediates >98-09-9
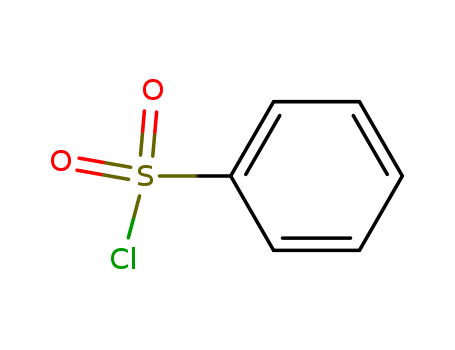

Product Details
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Insoluble and stable in cold water [Merck]. Decomposes in hot water to produce corrosive and toxic hydrochloric acid and benzenesulfonic acid. Rate of reaction decreases as temperature decreases. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
Benzenesulfonyl chloride is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents and bases, including amines. Corrodes metals in the presence of water due to slow formation of hydrochloric acid and benzenesulfonic acid [USCG, 1999]. May react vigorously or explosively if mixed with diisopropyl ether or other ethers in the presence of trace amounts of metal salts [J. Haz. Mat., 1981, 4, 291]. |
|
Health Hazard |
May be fatal if inhaled, swallowed or absorbed through skin. Contact may cause skin and eye burns. Irritating to eyes, skin and mucous membranes. INGESTION: May cause abdominal spasm and vomiting. |
|
Safety Profile |
Poison by intraperitoneal route. Adangerous storage hazard. It may explode in a sealedbottle. Explosive reaction with dimethyl sulfoxide. Reactsvigorously with methyl formamide. When heated todecomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl- and SO |
|
Potential Exposure |
It is used as a chemical intermediate for benzenesulfonamides, thiophenol, glybuzole (hypoglycemic agent), N-2-chloroehtylamides, benzonitrile; for its esters-useful as insecticides, and miticides. |
|
Shipping |
UN2225 Benzene sulfonyl chloride, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8—Corrosive material. |
|
Purification Methods |
Distil the sulfonyl chloride, then treat it with 3mole % each of toluene and AlCl3, and allow it to stand overnight. The sulfonyl chloride is distilled off at 1mm pressure and then carefully fractionally distilled at 10mm in an all-glass column. [Adams & Marvel Org Synth Coll Vol I 84 1941, Jensen & Brown J Am Chem Soc 80 4042 1958, Beilstein 11 IV 49.] It is TOXIC. |
|
Incompatibilities |
Violent reaction with strong oxidizers, dimethyl sulfoxide, and methyl formamide. It is very reactive with bases and many organic compounds. Incompatible with ammonia, aliphatic amines. Water contact forms hydrochloric and chlorosulfonic acids. Aqueous solutions of this chemical are strong acids that react violently with bases. Attacks metals in presence of moisture. |
|
General Description |
A colorless to slightly yellow solid that melts at approximately 40°F. Very irritating to skin, eyes and mucous membranes. May emit toxic fumes when heated to high temperatures. Used to make dyes and other chemicals. |
InChI:InChI=1/C6H5ClO2S/c7-10(8,9)6-4-2-1-3-5-6/h1-5H
-
The reaction of amines, N-substituted by...
Among external stimuli used to promote a...
We herein report a selective and catalyt...
A simple and rapid method for efficient ...
The NS2B/NS3 serine proteases of the Zik...
N,N-dimethyl-aniline

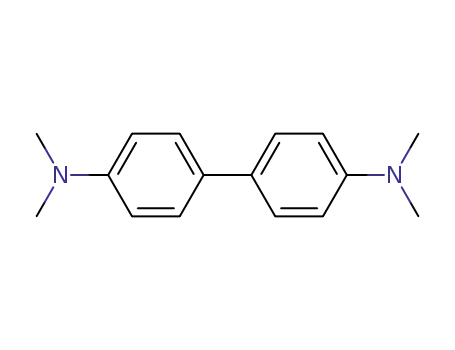
N,N,N',N'-tetramethylbenzidine
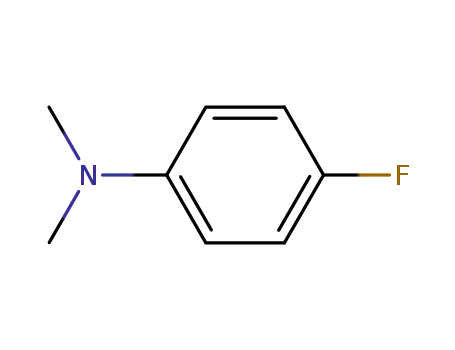
4-fluoro-N,N-dimethylaniline

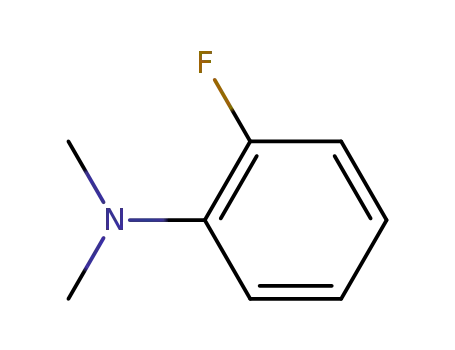
2-fluoro-N,N-dimethylaniline

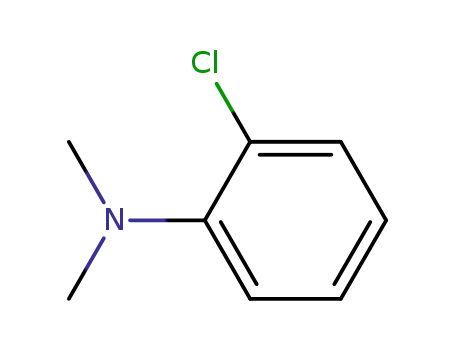
1-chloro-2-(dimethylamino)benzene

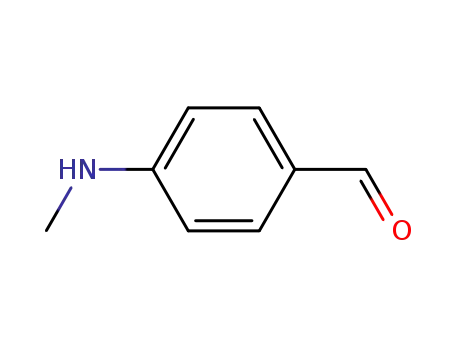
4-(methylamino)benzaldehyde

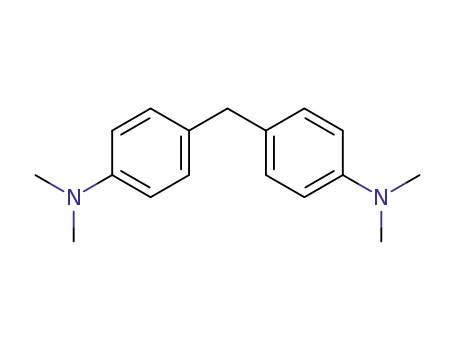
4,4'-methylene-bis(N,N-dimethylaniline)

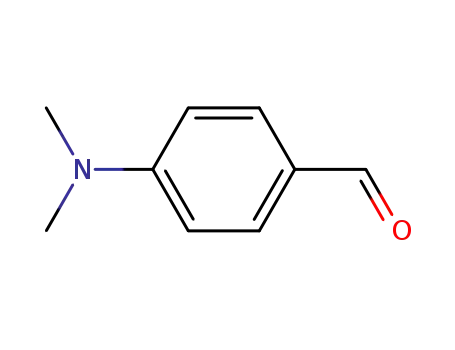
4-dimethylamino-benzaldehyde

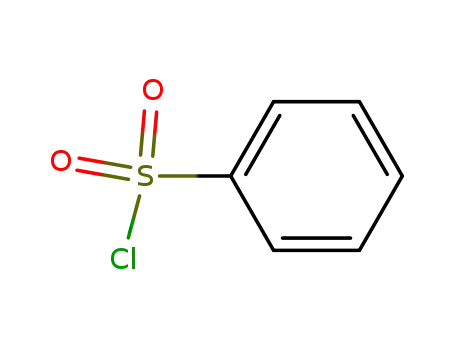
benzenesulfonyl chloride
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
zirconium(IV) chloride; N-fluorobis(benzenesulfon)imide;
In
chloroform;
for 5h;
Reflux;
|
6% |
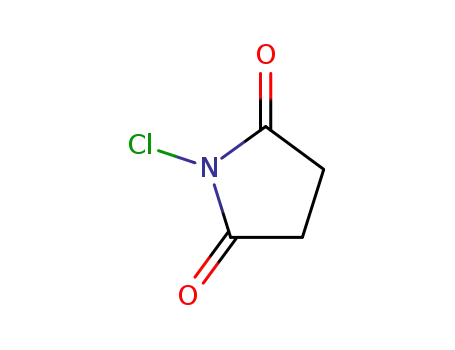
N-chloro-succinimide

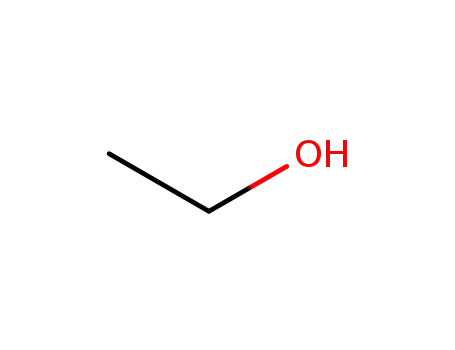
ethanol


Benzyl phenyl sulfide

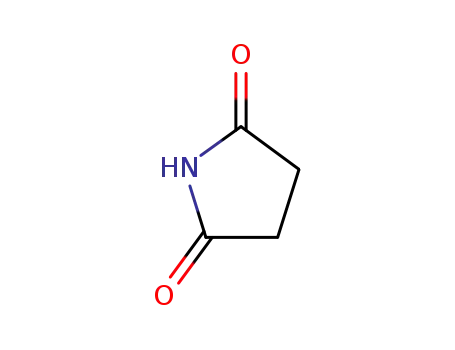
Succinimide

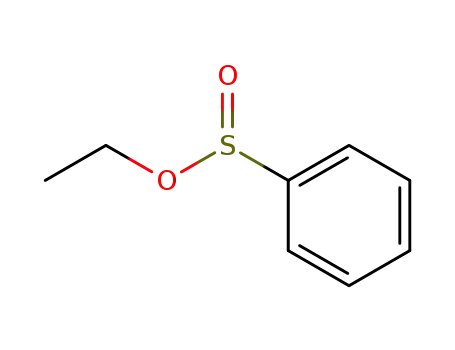
ethyl benzenesulfinate

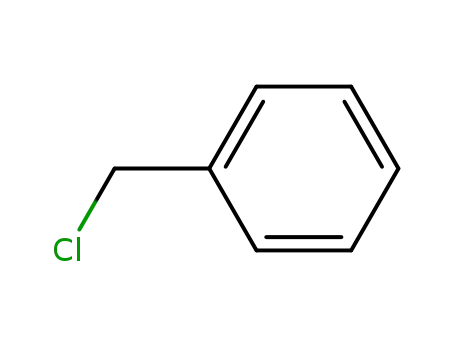
benzyl chloride


benzenesulfonyl chloride
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In
dichloromethane;
for 18h;
Product distribution;
Ambient temperature;
|
30% |
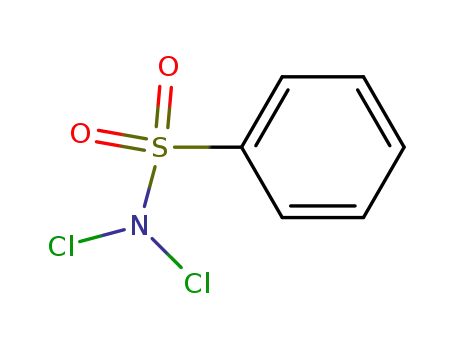
N,N-Dichlorobenzenesulfonamide
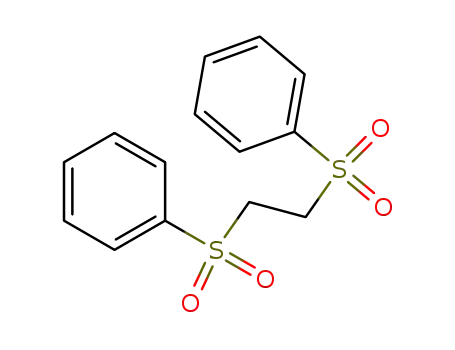
1,2-bis(phenylsulfonyl)ethane
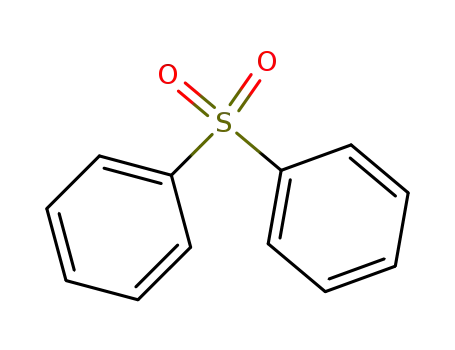
diphenyl sulphone
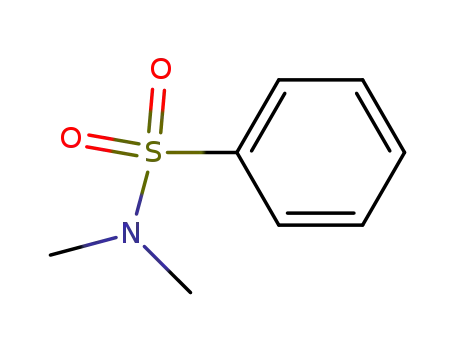
N,N-dimethylbenzenesulfonamide
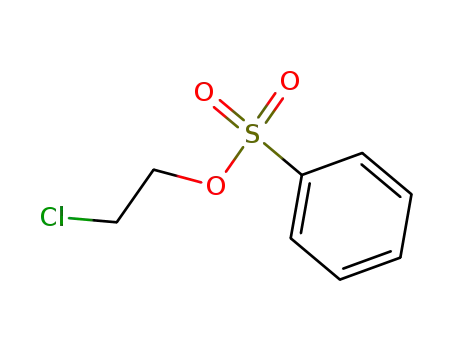
2-chloroethyl benzenesulfonate
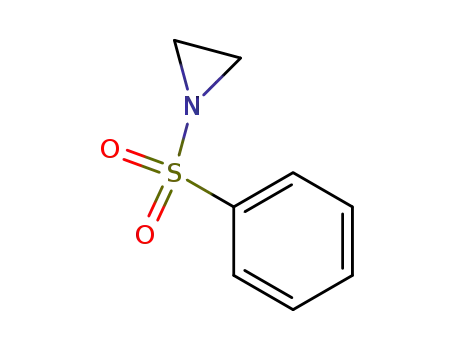
N-(phenylsulfonyl)aziridine
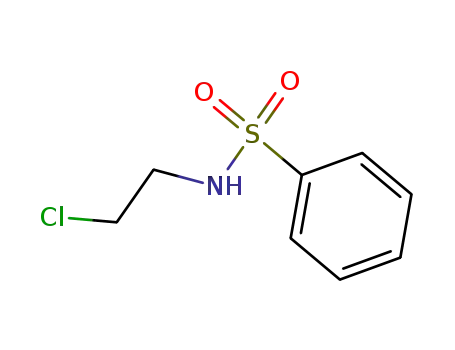
N-(2-chloro-ethyl)-benzenesulfonamide
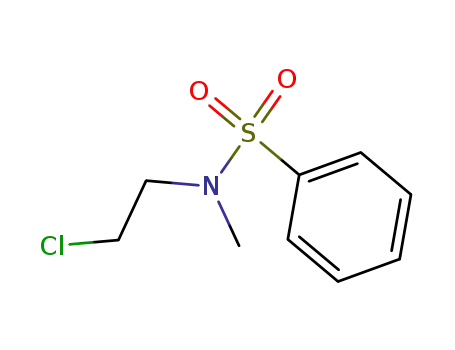
N-(2-chloro-ethyl)-N-methyl-benzenesulfonamide