
Antioxidant BHT 264
CAS:128-37-0
Purity:99%
Contact Now
We will contact you as soon as possible
Your Location:Home >Products >Industrial Chemicals >624-92-0

Product Details
|
Preparation |
Dimethyl disulfide can be prepared by the reaction between imethyl sulfate and sodium sulfide. under stirring, sulfur powder was added into sodium sulfide solution. The above reaction system was heated Up to 80-90℃, after reaction for 1 h, cooled to about 30 ℃. Dimethyl sulfate was dropped into the reaction system and the reaction was continued for 2h. Then, distillation, stratification, Separating waste alkali liquor, then through distillation and final products are prepared.In industry,dimethyl sulfate method is adopted to synthesize dimethyl disulfide.Na2S+S→Na2S2Na2S2+(CH3)2SO4→CH3SSCH3+Na2SO4From magnesium methyl iodide and S2Cl2, or from S2S2 and sodium methyl sulfate; also from methyl bromide and sodium thiosulfate, after which the resulting sodium methylthiosulfate is heated to yield dimethyl disulfide. |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Highly flammable. Slightly soluble in water. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
DMDS is a reducing agent. A dangerous fire hazard when exposed to oxidizing materials. Emits toxic fumes of oxides of sulfur when heated to decomposition or on contact with acids [Sax, 9th ed., 1996, p. 1320]. |
|
Health Hazard |
May cause toxic effects if inhaled or absorbed through skin. Inhalation or contact with material may irritate or burn skin and eyes. Fire will produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Vapors may cause dizziness or suffocation. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may cause pollution. |
|
Fire Hazard |
HIGHLY FLAMMABLE: Will be easily ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Vapors may form explosive mixtures with air. Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Most vapors are heavier than air. They will spread along ground and collect in low or confined areas (sewers, basements, tanks). Vapor explosion hazard indoors, outdoors or in sewers. Runoff to sewer may create fire or explosion hazard. Containers may explode when heated. Many liquids are lighter than water. |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Highlyflammable |
|
Safety Profile |
Poison by inhalation. A very dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat, flame, or oxidzers. Can react vigorously with oxiduing materials. See also SULFIDES. |
|
Purification Methods |
Pass it through neutral alumina before use. [Trost Chem Rev 78 363 1978, Beilstein 1 IV 1281.] |
|
Toxicity evaluation |
Very little information is available on mechanism of toxicity. Although the authors of one experimental animal study suggested that methyl disulfide toxicity resembles that of hydrogen sulfide, it is not at all clear that cytochrome oxidase inhibition can result from methyl disulfide exposure. Mechanistically hydrogen sulfide is classified as a chemical asphyxiant because of its known ability to disrupt electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation by interaction with the enzyme cytochrome oxidase. Other sources classify methyl disulfide a simple asphyxiant, which means that it is nonreactive with enzymes or other cell components and simply displaces oxygen in the air. Some information indicates that neurotoxicity to insects results when methyl disulfide disrupts calcium-activated potassium channels in insect pacemaker neurons. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: Dimethyl disulfide is an organic disulfide that is methane in which one of the hydrogens has been replaced by a methyldisulfanyl group. It has a role as a xenobiotic metabolite. |
|
Aroma threshold values |
Detection: 0.16 to 1.2 ppb. Recognition: 90 ppb |
|
General Description |
A colorless oily liquid with a garlic-like odor. Denser than water and slightly soluble in water. Flash point 40°F. Vapors heavier than air. May irritate skin and eyes. Used to make other chemicals. |
InChI:InChI=1/C2H6S2/c1-3-4-2/h1-2H3
The reactivity of the prototypical phosp...
UV and IR absorption cross sections were...
The role of amino acids and α-dicarbonyl...
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is widely used...
Porous carbon spheres with high surface ...
Several recent studies have shown unique...
4-nitrophenyl azide

dimethylsulfide

Dimethyldisulphide

![2-[(methylthio)methyl]-4-nitroaniline](/upload/2025/1/410220cd-8ac3-4481-ac68-37019cb7df0c.png)
2-[(methylthio)methyl]-4-nitroaniline

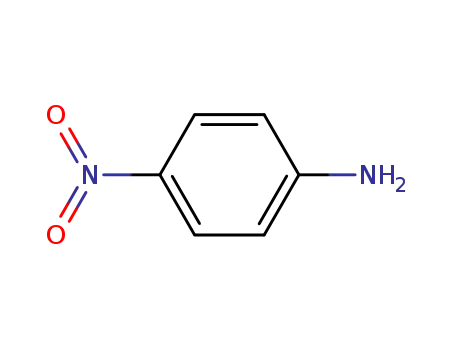
4-nitro-aniline
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
at 155 ℃;
for 10h;
|
15% 39% |
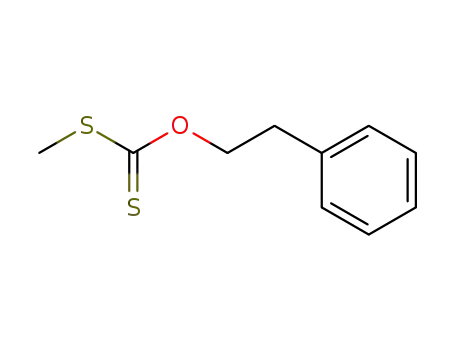
S-methyl O-phenylethyl carbonodithioate


Dimethyldisulphide

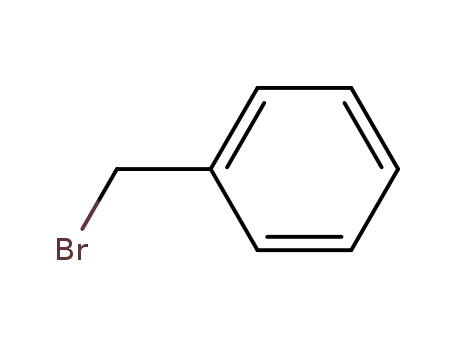
benzyl bromide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
copper(ll) bromide;
In
acetonitrile;
for 5.7h;
Product distribution;
Ambient temperature;
var. solvents, CuCl2, other xanthate esters,;
|
63% |
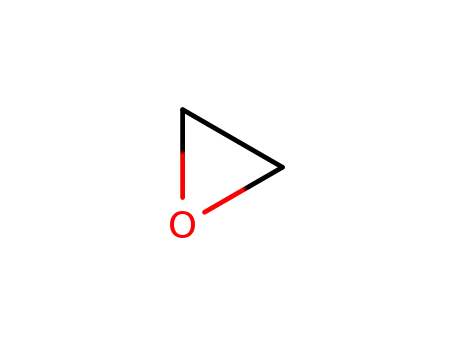
oxirane
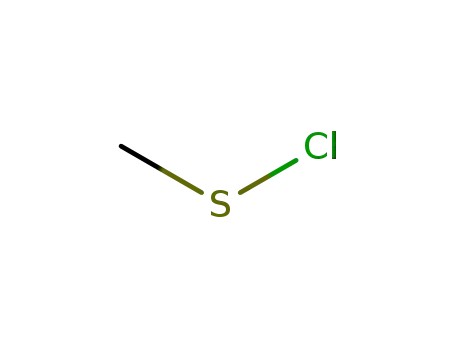
Methanesulfenyl chloride
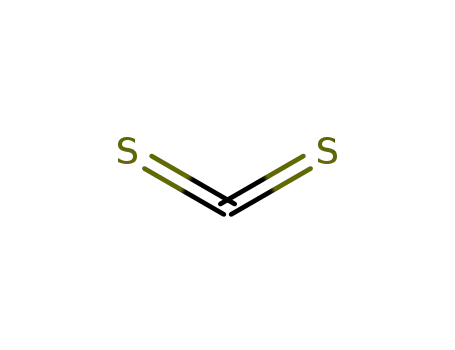
carbon disulfide
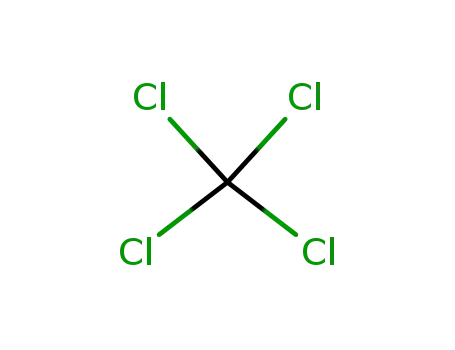
tetrachloromethane
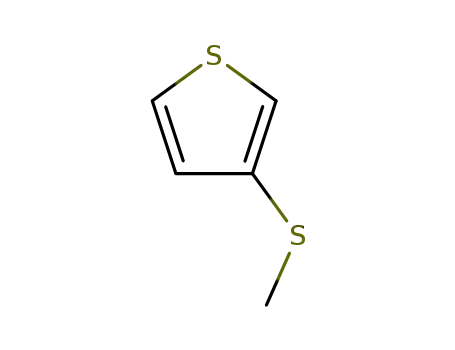
3-(methylthio)thiophene
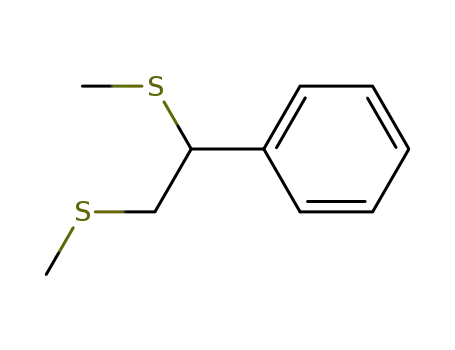
1,2-bis(methylthio)phenylethane
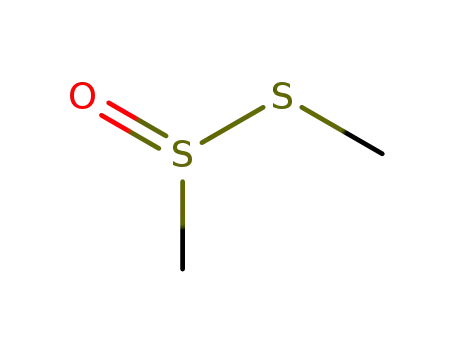
S-methyl methanethiosulfinate
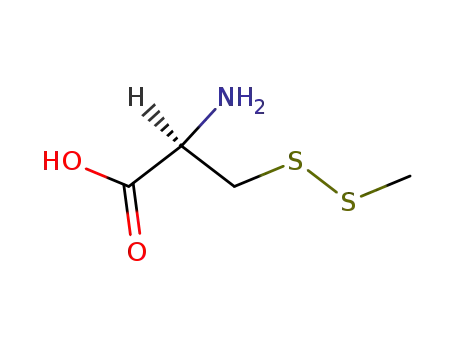
S-(methylthio)-L-cysteine