
Antioxidant BHT 264
CAS:128-37-0
Purity:99%
Contact Now
We will contact you as soon as possible
Your Location:Home >Products >Pharmaceutical API >175481-36-4

Product Details
|
Generic formulation |
MHRA/ CHM advice to minimize risk when switching patients with epilepsy between different manufacturers’ products (incl. generic products): It is usually unnecessary to ensure that patients are maintained on a specific manufacturer’s product unless there are specific concerns, such as patient anxiety and risk of confusion/ dosing error. |
|
Indications |
Epilepsy: Adjunctive treatment of focal seizures with or without secondary generalization. |
|
Dose titration |
Epilepsy— adjunctive therapy: 50 mg bd for 7 days, then increased by 50 mg bd every 7 days; usual maintenance 100 mg bd (max. 200 mg bd). Epilepsy— adjunctive therapy (loading dose regimen when it is necessary to rapidly attain therapeutic plasma concentrations, under close medical supervision): 200 mg bd for 1 day, followed by maintenance dose of 100 mg bd after 1 day, then increased if needed by 50 mg bd every 7 days (max. 200 mg bd). |
|
Side effects |
Lacosamide was generally well tolerated in adult patients with partial-onset seizures.[11] The side-effects most commonly leading to discontinuation were dizziness, ataxia, diplopia (double vision), nystagmus, nausea, vertigo and drowsiness. These adverse reactions were observed in at least 10% of patients.[9] Less common side-effects include tremors, blurred vision, vomiting and headache. |
|
Cautions |
Patients with conduction problems (contraindicated in patients with second- or third- degree A– V block). Patients with severe cardiac disease. Patients at risk of PR- interval prolongation. Elderly patients. |
|
Interactions |
With AEDs Concomitant treatment with other AEDs known to be enzyme inducers (such as carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin) decreases the overall systemic exposure of lacosamide by 25%. With other drugs Nil. With alcohol/food Although no pharmacokinetic data on the interaction of lacosamide with alcohol are available, a pharmacodynamic effect cannot be excluded. There are no specific foods that must be excluded from diet when taking lamotrigine. |
|
Special populations |
Hepatic impairment Titrate with caution in mild- to- moderate impairment if co- existing renal impairment. Caution in severe impairment. Renal impairment Loading dose regimen can be considered in mild- to- moderate impairment (titrate above 200 mg with caution). Titrate with caution in severe impairment (max. 250 mg daily). Pregnancy There are no adequate data from the use of lacosamide in pregnant women and the potential risk for humans is unknown. Lacosamide should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly necessary (if the benefit to the mother clearly outweighs the potential risk to the foetus). If a woman decides to become pregnant, the use of lacosamide should be carefully re- evaluated. In case of treatment with lacosamide, the dose should be monitored carefully during pregnancy and after birth, and adjustments made on a clinical basis. Lacosamide has been found to be present in milk in animal studies and it is recommended that it should be avoided during breastfeeding |
|
Behavioural and cognitive effects in patients with epilepsy |
For this third- generation agent, clinical experience is still limited and little is known about its positive and negative psychotropic properties and their implications for the management of behavioural symptoms in patients with epilepsy. There are initial reports of depression, irritability and agitation, and psychotic symptoms. Reports of cognitive effects (mainly affecting attention and memory) are rare and usually not severe. |
|
Psychiatric use |
Lacosamide has no indications for the treatment of psychiatric disorders. There is insufficient experience with lacosamide to draw any conclusion regarding its psychotropic profile. |
|
Synthesis |
The most common adverse events were diplopia, headache, dizziness, and nausea. As typical with AEDs, lacosamide may increase the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior. Patients should, therefore, be monitored for the emergence or worsening of depression. Caution should also be exercised in patients with known conduction problems or severe cardiac disease (myocardial ischemia or heart failure) since dose-dependent prolongations in PR interval have been observed in clinical studies. |
|
Drug interactions |
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs Antidepressants: anticonvulsant effect antagonised; avoid with St John’s wort. Antimalarials: mefloquine antagonises anticonvulsant effect. Antipsychotics: anticonvulsant effect antagonised. Orlistat: possibly increased risk of convulsions. |
|
Metabolism |
The metabolism of lacosamide has not been completely characterised. Lacosamide is a CYP2C19 substrate. Metabolites are inactive. About 95% of a dose is excreted in the urine, about 40% as unchanged drug and less than 30% as the inactive O-desmethyl metabolite. Less than 0.5% of a dose is excreted in the faeces |
|
Brand name |
Vimpat |
InChI:InChI=1/C13H18N2O3/c1-10(16)15-12(9-18-2)13(17)14-8-11-6-4-3-5-7-11/h3-7,12H,8-9H2,1-2H3,(H,14,17)(H,15,16)/t12-/m1/s1
A short and highly efficient synthetic a...
An efficient total synthesis of (R)-laco...
A catalytic enantioselective three-compo...
An efficient and scalable synthesis of t...
Total synthesis of anticonvulsant amino ...
The invention relates to a preparation m...
The invention discloses a new synthesis ...
A direct and highly enantioselective rea...
The invention provides a novel methylati...

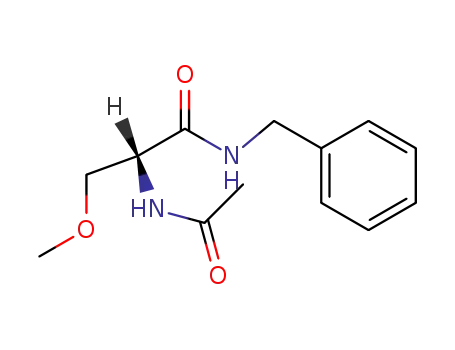
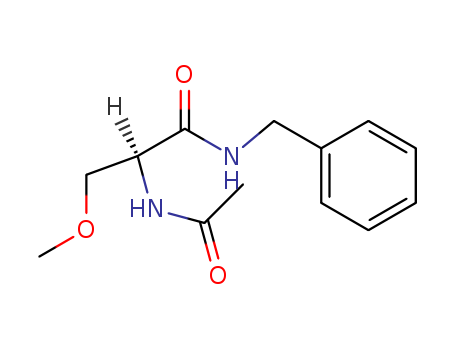
lacosamide
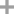
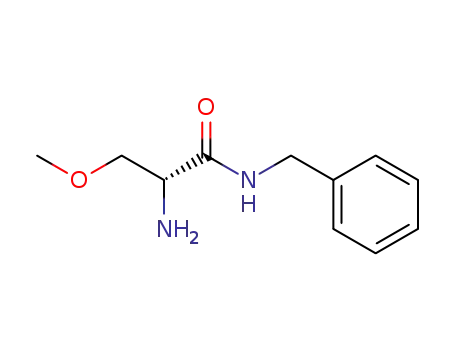
(R)-2-amino-N-benzyl-3-methoxypropanamide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
|
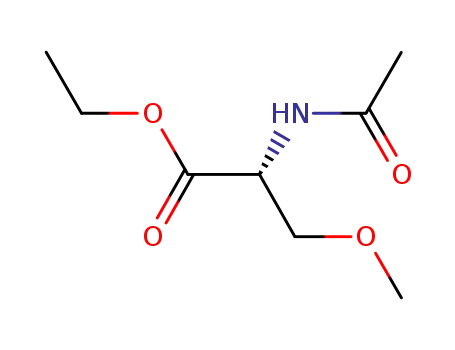
N-acetyl-β-methoxy-D-alanine ethyl ester

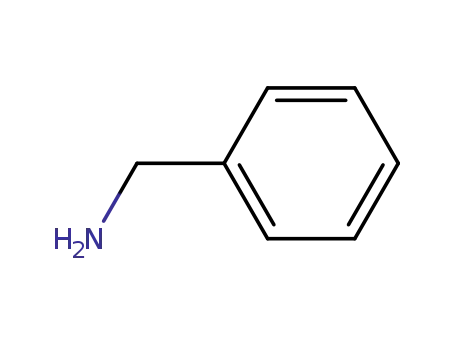
benzylamine


lacosamide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
benzylamine;
With
trimethylaluminum;
In
dichloromethane;
at 20 ℃;
for 0.166667h;
Inert atmosphere;
N-acetyl-β-methoxy-D-alanine ethyl ester;
In
dichloromethane;
for 3h;
Inert atmosphere;
|
94% |
|
In
methanol;
for 18h;
Reflux;
|
80% |
|
benzylamine;
With
trimethylaluminum;
In
dichloromethane;
for 0.5h;
N-acetyl-β-methoxy-D-alanine ethyl ester;
In
dichloromethane;
for 3h;
|
78% |
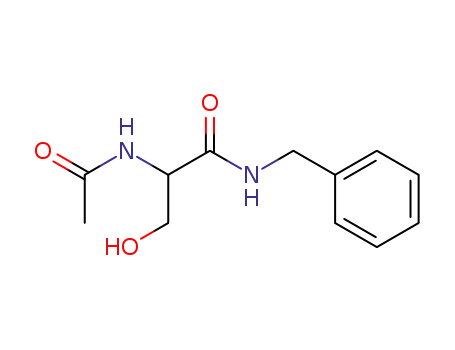
(R,S)-N-acetylserine-N-benzylamide
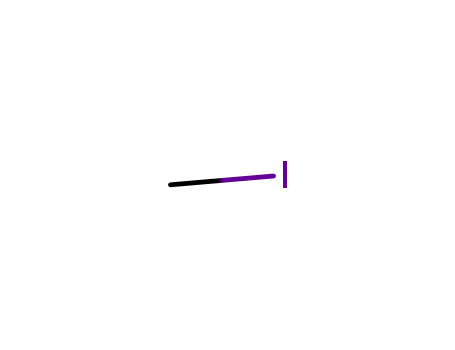
methyl iodide
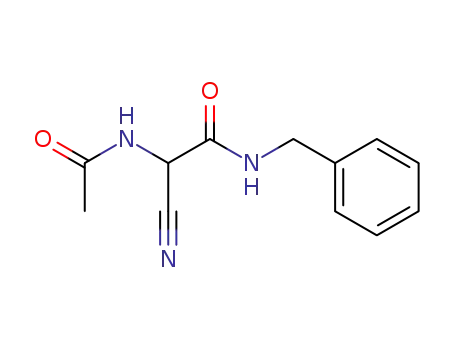
α-acetamido-N-benzyl-α-cyanoacetamide
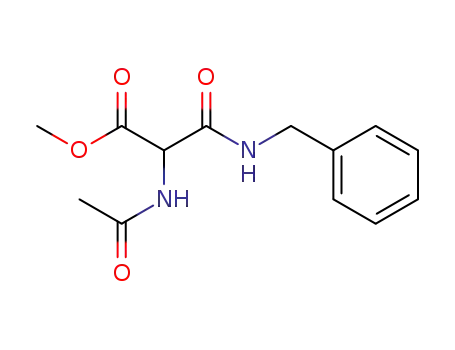
methyl α-acetamido-N-benzylmalonamate
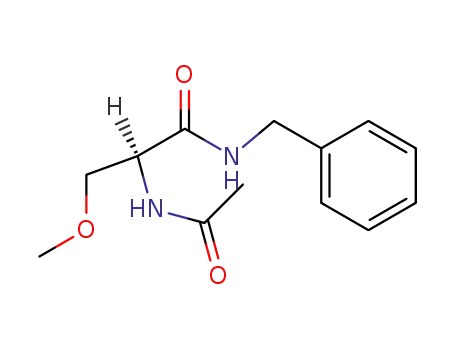
(2S)-2-(acetylamino)-N-benzyl-3-methoxypropanamide

lacosamide
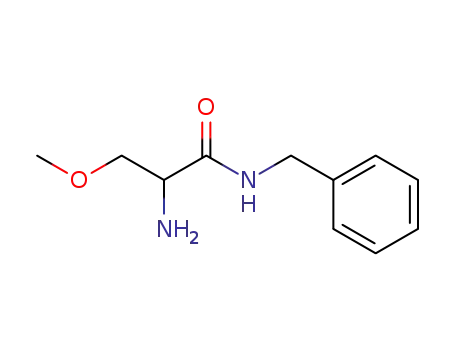
N-Benzyl-2-Amino-3-Methoxypropionamide
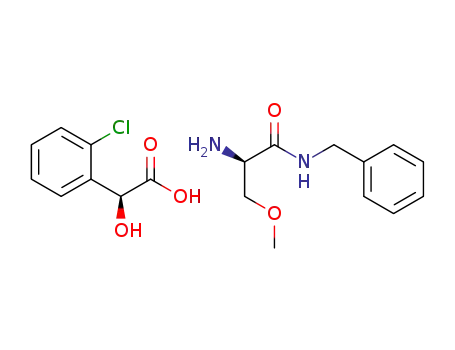
C8H7ClO3*C11H16N2O2