
Antioxidant BHT 264
CAS:128-37-0
Purity:99%
Contact Now
We will contact you as soon as possible
Your Location:Home >Products >Thermal Paper Chemicals >127-63-9
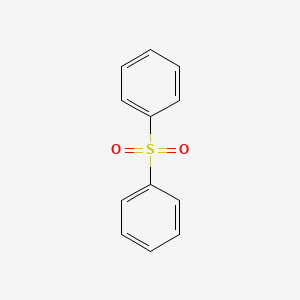

Product Details
|
Chemical Properties |
Diphenyl sulfone is a sulfone compound having two S-phenyl substituents. It is a crystalline powder that is soluble in organic solvents. It has been found in plants like Gnidia glauca and Dioscorea bulbifera. It has a role as a plant metabolite. Diphenyl sulfone is formed under certain conditions by the action of aqueous sulfuric acid on benzene. It is used as a high temperature solvent. Such high temperature solvents are useful for processing highly rigid polymers, e.g., PEEK, which only dissolve in very hot solvents. |
|
Uses |
Diphenyl sulfone is a white, solid organosulfur compound, has a boiling point of 714.2 °F (379 °C) and is soluble in organic solvents. Diphenyl sulfone is used as a high temperature solvent for processing rigid polymers that only dissolve in very hot solvents, such as PEEK. It is also used in coating products, paper chemicals, and dyes. Diphenyl sulfone, a well-known strong electron acceptor, can form D-A structured compounds when connected with different donor substituents such as carbazole, diphenylamine, or acridine groups. These D-A compounds are extensively employed as thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) emitters, host or transport materials in organic light-emitting diodes, but almost none of them have been applied in electrochromism. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: A sulfone compound having two S-phenyl substituents. It has been found in plants like Gnidia glauca and Dioscorea bulbifera. |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Diphenyl sulfone can be flammable and explosive under certain conditions: Dust clouds: Fine dust (420 microns or less) created by grinding diphenyl sulfone can ignite and burn quickly and fiercely. Larger particles up to 1400 microns in diameter can also contribute to an explosion. Dust clouds can only ignite within a specific concentration range, similar to gases and vapors. Autoignition: Diphenyl sulfone has an autoignition temperature of over 475°C. |
|
Purification Methods |
Crystallise the sulfone from diethyl ether. It has been purified by zone melting. [Beilstein 6 H 300, 6 IV 1490.] |
InChI:InChI=1/C12H10O2S/c13-15(14,11-7-3-1-4-8-11)12-9-5-2-6-10-12/h1-10H
A series of multicolored cathodically coloring electrochromic (EC) materials based on diphenyl sulfone (DPS) moiety were synthesized and characterized. Herein two electron donors, N1,N1,N3,N3-tetraphenylbenzene-1,3-diamine (TPA) and 1,3-di (9H-carbazol-9-yl)benzene (MCP), were employed to construct donor-acceptor (D-A) or donor-acceptor-donor (D-A-D) small molecules with DPS as the acceptor.
Designing an active site: A new type of ...
Diphenyl sulfoxide-35S was reduced to the sulfide-35S nearly quantitatively by heating with sulfur at 280°C, while diphenyl sulfone did not react with sulfur at the same temperature. At around 300°C, diphenyl sulfone-35S started to react with sulfur and gave diphenyl sulride that lost nearly 75% of the original activity of 35S of the sulfone used. The main reaction of the sulfone was found not to be reduction, but substitution involving induced C-S cleavage and replacement with sulfur chain.
Effect of different reaction parameters ...
Two anionic and coordinatively saturated...
chlorosulfonate de trimethylsilyle

benzene

diphenyl sulphone

trimethylsilyl benzenesulfonate
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
at 80 ℃; for 10h; Product distribution; also with other three alkylsubstituted and one halogensubstituted aromatic hydrocarbons;
|
24% 71% |
Benzolpyrosulfonsaeure-trimethylsilylester

benzene

diphenyl sulphone

trimethylsilyl benzenesulfonate

Bis(trimethylsilyl)sulfat

benzenesulfonic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
at 80 ℃; for 3h;
|
11% 39% 41% 11% |
Perbenzoic acid
chloroform
diphenyl sulfide
diethyl ether
hexaphenyldisiloxanne
tetraphenylsilane
hexa-Si-phenyl-Si,Si'-m-phenylene-bis-silane
triphenylhydroxysilane